
GeMTeX creates first standard for de-identification of German medical documents
In the GeMTeX project of the Medical Informatics Initiative (MII), an interdisciplinary team is working to make texts from clinical routine care available for research and clinical use. The goal is to create one of the largest datasets for automatic processing of German-language medical texts. The GeMTeX team has now reached an important milestone: for the first time, researchers from the University Hospitals of Leipzig and Erlangen have published annotations for a text corpus, which serve as a template for the de-identification of German medical texts. Annotations are markers for text passages that provide metadata about the content. These markers make the texts usable for applications such as artificial intelligence and large language models.
Pilot study on the annotation of personal health information
In the process of de-identification, data that could allow conclusions to be drawn about individuals is rendered unrecognizable. In a pilot study, medical students from the Universities of Leipzig and Erlangen, together with a team of experts from the fields of linguistics, medicine and computer science, annotated 1,438 fictitious doctor’s letters. The letters were taken from the Graz Synthetic Text Corpus (GRASCCO).
During the annotation process, the GeMTeX team focused on text passages containing sensitive information such as names, dates, addresses, or professions. These annotations make it possible to adapt software to automatically detect and encrypt personal health information in clinical documents.
An example of privacy-compliant processing of medical texts
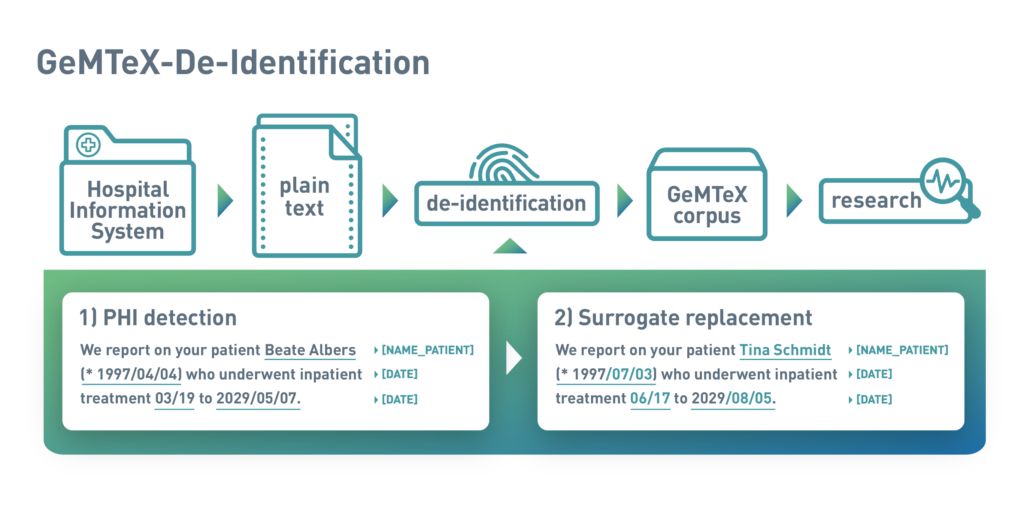
The annotated documents have been published on the international research data platform Zenodo and are intended to serve as a template for future projects. Together with the annotated corpus, a publication was published that describes a procedure for de-identification of medical documents. The de-identification pipeline consists of the following steps:
- Exporting the clinical texts as raw data from the local hospital information system
- Import into the INCEpTION annotation platform
- Automated pre-annotation of relevant text passages with identifying information by the Averbis Health Discovery Pipeline
- Manual review and correction of annotations using the dual control principle
- Automated replacement of pre-annotated and corrected data with appropriate pseudonyms (see figure)
The results of the pilot study have been summarized in a publication.
Link to the publication in PubMed
Link to the annotated text corpus and annotation guidelines (Zenodo)

